InnerBoundary
This parameter can be set either to
'WALL' (or 'RIGID'), 'OPEN', or 'NON-REFLECTING'. It specifies
the boundary condition at the inner boundary. 'WALL' or 'RIGID' sets
the radial velocity to zero at the boundary. No material can flow from
or to the mesh : the disk total gaseous mass is conserved (the outer
boundary has a 'WALL' condition by default as well). 'OPEN' implies
that the material can flow outside of the mesh, on its way to the
central object : the total gaseous mass decreases with time.
'NON-REFLECTING' applies a transmitted wave boundary condition, as
follows: the pitch angle of the wake at the boundary is evaluated using
a WKB approximation. The content of the border ring is then
copied into the ghost ring, properly azimuthally shifted by the amount
dictated by the pitch angle. This technique is very efficient at
removing any reflected wave, but it evaluates only one pitch angle,
assuming the planet to have a semi-major axis a=1, so it efficiently only removes
the reflected wake of this planet. Note that the non-reflecting
boundary condition is also applied at the outer boundary, and that this
condition does not strictly conserve the disk mass and angular momentum
(the transmitted wave carries away some angular momentum from the mesh).
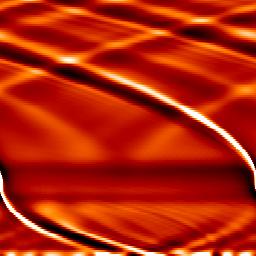
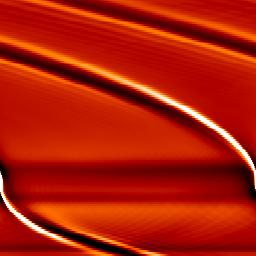
The figures below show the disk response to an embedded Saturn-mass planet after a few tens of orbits, at the same date and with strictly the same parameters, but with different boundary conditions.
Note that it is not possible to independently select the outer boundary and inner boundary conditions. There is no OuterBoundary parameter. This is a shortcoming of Fargo, but in practice it has never been needed. In case this is needed, it is however straightforward to implement (see src/SideEuler.c).
The figures below show the disk response to an embedded Saturn-mass planet after a few tens of orbits, at the same date and with strictly the same parameters, but with different boundary conditions.
 |
 ' ' |
| 'Wall' boundary conditions |
'Non-reflecting' boundary conditions |
Note that it is not possible to independently select the outer boundary and inner boundary conditions. There is no OuterBoundary parameter. This is a shortcoming of Fargo, but in practice it has never been needed. In case this is needed, it is however straightforward to implement (see src/SideEuler.c).